
Learn and engage this Disability Pride Month
Disability Pride Month is celebrated every July to honor the history, achievements, experiences and struggles of the disability community in recognition of the anniversary of the Americans with Disabilities Act, landmark legislation that broke down barriers to inclusion in society.
Disability Pride Month was officially established in July 2015, on the 25th anniversary of the ADA, by cities across the country with parades, festivals, educational opportunities and advocacy events. Many embrace the idea of disability pride as a grassroots movement challenging systemic ableism and the pervasive stigmatization of disability.
Ableism is the discrimination of and social prejudice against people with disabilities based on the belief that typical abilities are superior. Abelist microaggressions are the everyday slights, indignities and insults that disabled people experience in their day-to-day interactions.
People with disabilities are the largest and most diverse minority within the U.S. population, representing all abilities, ages, races, ethnicities, religions and socioeconomic backgrounds. According to the CDC, one in four Americans has a disability. Worldwide, about one billion people—or 15% of humanity’s population—live with a disability.
Despite this prevalence, stigmas about disabilities and the people who have them are pervasive, and barriers to opportunity and full participation in society exist.
What is the ADA?
The Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) protects people with disabilities from discrimination. It was signed into law on July 26, 1990, by President George H.W. Bush. July 26 is federally recognized as National Disability Independence Day.
The law requires employers to provide equal opportunities and benefits to those with disabilities and prohibits companies from not hiring someone based on perceived or actual disability. It also protects those with a history of disability, such as someone who had cancer that is in remission.
The ADA requires employers to offer reasonable accommodation for their employees’ disabilities. This might include providing a sign language interpreter or captioner in a virtual meeting, offering multi-sensory learning opportunities or installing wheelchair ramps.
Anywhere the public is welcome, an individual with a disability should also be welcome and able to enter and participate—regardless of mobility aid use, disability or the presence of a service animal.
Modeled on other civil rights laws prohibiting discrimination based on race, sex, color, age, national origin or religion, the ADA guarantees Americans with disabilities the right “to equal opportunity.”
In 2008, Congress passed the ADA Amendments Act to modify the narrow way courts were defining disability, refocusing the issue not on what disability is but on whether discrimination occurred.
Indeed, the ADA has become a global model for disability access and inclusion. But despite its anti-discrimination laws and the many examples of institutional and private enterprise initiatives to increase workplace equity and inclusion, disability discrimination still exists—often in the form of ableist microaggressions.
Our society’s long history of discrimination against people with disabilities continues to translate to their unemployment and underemployment: the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics found that “across all age groups, persons with disabilities were much less likely to be employed than those with no disabilities.”
The diversity of disabilities
As with all demographic groups, the disability community is not a monolith, but rather a diverse group of people with a wide range of needs. Disability spans all abilities, ages, races, ethnicities, religions and socioeconomic backgrounds and can be seen or unseen. Moreover, people with disabilities may hold dramatically different viewpoints and perspectives from one another on any number of issues and topics.
Mental health disorders are the most prevalent types of disability in the U.S.
Some people with physical disabilities who wear smaller medical devices—such as Type 1 diabetics who wear continuous glucose monitors or insulin pumps—can choose how visible they want their disability to be. The same is true for individuals with any number of disabilities: autoimmune disorders, developmental differences, long COVID, migraines, anxiety, depression, diabetes, PTSD, heart disease, IBS, epilepsy, learning differences, and differences in neurological functioning and sensory perception.
And intellectual and developmental disabilities (IDD) is an umbrella term for differences, usually present at birth, as diverse as ADHD, Autism Spectrum Disorder, Down Syndrome, Tourette Syndrome, vision impairment, Cerebral Palsy, Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder and Muscular Dystrophy. Meet people with IDDs.
The Disability Pride flag
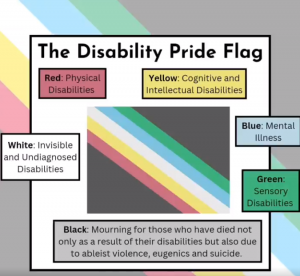 The Disability Pride flag shows a straight diagonal banner of five colors on a dark background. Its current design is an update of the original version of the banner with zigzag lines, which created a strobe effect on some computer and phone screens and caused difficulties for people with seizures and migraines.
The Disability Pride flag shows a straight diagonal banner of five colors on a dark background. Its current design is an update of the original version of the banner with zigzag lines, which created a strobe effect on some computer and phone screens and caused difficulties for people with seizures and migraines.
The design of the flag is intentionally inclusive of diverse disabilities. The diagonal stripes represent intercommunal solidarity in cutting across barriers, in contrast to what the designer, Ann Magill, sees as the traditional vertical walls and horizontal ceilings that keep disabled people isolated.
The colors used represent all six standard international flag colors to signify that the disability community is wide-reaching—but muted to lessen a nausea trigger for those who suffer from migraines and with red and green clearly separated to help those with color blindness. Each color represents a different type of disability: physical (red), cognitive and intellectual (yellow), invisible and undiagnosed (white), psychosocial (blue), and sensory (green).
Finally, the charcoal background symbolizes mourning and rage for the victims of ableist violence and abuse.
Learn more and get involved
Meet people in the UW community with disabilities:
- Fostering inclusivity through accessibility: Meet Ian Campbell
- All kinds of brains should be accommodated: Meet Lucas Harrington of the UW Autism Center
- People of UW: Meet disability justice advocate Christine Lew
- UW professor Stephanie Kerschbaum asks readers to challenge how they notice disability in new book
The UW Student Disability Commission is a student run and led advocacy organization committed to serving students, staff and faculty with disabilities at UW. The SDC understands disability as not merely an individual or medical problem, but rather the result of attitudinal and physical barriers preventing full participation in society.
Learn:
- About key moments in the Disability Rights Movement from UC Berkley’s archive on disability rights.
- Identity-first language is a popular article from the Autistic Self-Advocacy Network explaining the nuances of people-first versus identity-first language.
- Meet the top disability activists to know and follow hashtags such as #DisabilityRights, #SpoonieCommunity, #DisabilityPride, #Accessibility, #RightsOnFlights and #IStayStrong for a window into the experiences, concerns, and triumphs of disabled individuals.
- Review these etiquette basics for interacting with people with disabilities in the workplace (or anywhere) from nonprofit AmeriDisability.
- Talk to your family about disability and how to foster inclusion with these age-appropriate tips from Seattle Children’s.
Watch and read media that has been created by and with people with disabilities:
- Crip Camp is an Oscar-nominated film about a summer camp for disabled people that chronicles the stories of some of the camp attendees and how the conversations sparked there led to the modern disability justice movement.
- CODA is the story of a CODA (child of deaf adults) who discovers her passion for singing and must choose between her family obligations and her dreams. Winner of three Academy Awards.
- Art Enables, an art gallery and vocational arts program dedicated to creating opportunities for artists with disabilities to make, market, and earn income from their original and compelling artwork.
- Black Disabled Creatives is a platform created by disabled model Jillian Mercado.
- More excellent books about disabilities.
- Discover NEH-funded projects that expand disability access and research and support the teaching and preservation of disability history and experience.
- Check out to this inspiring TedX talk by disability advocate Wesley Hamilton, founder of Disabled But Not Really or this TedX talk by Diversability founder Tiffany Yu.
Check out these local organizations (and more below):
- Seattle Adaptive Sports – This organization provides sports and recreation opportunities for individuals with physical disabilities, including adaptive skiing, kayaking, and wheelchair basketball.
- The Washington Disability Inclusion Network, open to all state employees and their allies, has a mission to engage the experience, values and knowledge of people with disabilities in state government, promote universal access, and create an environment where people with disabilities can fully participate in all aspects of the workplace.
- Northwest ADA Center – This organization provides information, training, and technical assistance on the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) to individuals, businesses, and organizations in the Northwest region.
- DAWN – Disabilities Awareness and Advocacy Network – This organization provides advocacy, education, and support services to individuals with disabilities, including peer support groups and employment services.
Support
Consider making a one-time contribution or setting up payroll deduction to a UWCFD member organization that centers disabled people and the causes that impact them:
University of Washington DO-IT Program Fund (charity code 1481184): UW’s Do-IT (Disabilities, Opportunities, Internetworking, and Technology) Center is dedicated to empowering people with disabilities through technology and education. It promotes awareness and accessibility—in both the classroom and the workplace—to maximize the potential of individuals with disabilities and make our communities more vibrant, diverse, and inclusive.
The UW Autism Center (charity code 1481191) provides professional training, diagnostic evaluation and program consultation for children with autism and related pervasive developmental disorders.
The Arc of King County (charity code 0315598): The Arc of King County promotes and protects the rights of people with intellectual and developmental disabilities so they can live, learn, work and play in the community – improving the quality of life for us all.
Easter Seals Washington (charity code 0315936): Changing the way the world defines and views disabilities by making profound, positive differences in people’s lives every day.
Disability Rights Washington (charity code 1481504): Our mission is to advance the dignity, equality, and self-determination of people with disabilities. We pursue justice on matters related to human and legal rights.
Summit Assistance Dogs (charity code 0315210) creates life-changing partnerships by providing highly skilled mobility service dogs for people living with disabilities in the Pacific Northwest.
Kindering (charity code 0315445): Kindering embraces children of diverse abilities and their families by providing the finest education and therapies to nurture hope, courage, and the skills to soar.
Wonderland Kinds (charity code 1478424): is a nonprofit agency serving children with developmental delays, disabilities, and prenatal substance exposure. Founded in 1969, Wonderland is dedicated to helping children meet healthy developmental milestones.
Born this Way Foundation (charity code 1482977): supports the mental health of young people and works to create a kinder braver world through high impact programming, youth led conversations, and strategic partnerships.
Bridgeways (charity code 1478773): offers services that promote quality of life for individuals living with mental illness in a manner that facilitates growth, independence, and a sense of community.
Youth Outdoors Unlimited (charity code 1481547): is organized to take youth diagnosed with a life-threatening illness and/or physical disability who have to dream to hunt or fish on their own fully funded outdoor adventure.
2 Thoughts on “Learn and engage this Disability Pride Month”
On July 10, 2023 at 3:13 PM, Annie said:
Hi Nicole, thanks for the awesome article and extensive resource list! About the Town Hall Seattle event on Friday, July 23: I have seen this event advertised a couple times now, but I noticed that the 23rd is not a Friday, and your link points to a past event from 2021. Do you know if Town Hall Seattle will have a Disability Pride Month event again this year?
On July 10, 2023 at 6:54 PM, Nicole Reeve-Parker said:
Annie, good catch! Thank you. I couldn’t find any Town Hall Seattle events for 2023, alas, so I deleted it. If you come across any events of interest in the Puget Sound area, please let me know!
Comments are closed.